Technology
| all | Safety Management of Ultraviolet Radiation(R2) |
|---|
1. Introduction
Ultraviolet radiation is harmful to the human body, particularly causing disturbance in the functions of eye and skin. The degree of irradiation risks varies depending on the wavelength of radiation, and its details have been clarified today.
As human eyes are most susceptible to ultraviolet radiations, we consider eyes as the most important organ for us to protect from exposure.
Table 1. Permitted Tolerant Exposure
| Wavelength (nm) |
TLV (mJ/cm2) |
Relative hazardous ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | 100 | 0.03 |
| 210 | 40 | 0.075 |
| 220 | 25 | 0.12 |
| 230 | 16 | 0.19 |
| 240 | 10 | 0.30 |
| 250 | 7.5 | 0.43 |
| 254 | 6.0 | 0.5 |
| 260 | 4.6 | 0.65 |
| 270 | 3.0 | 1.0 |
| 280 | 3.4 | 0.88 |
| 290 | 4.7 | 0.64 |
| 300 | 10 | 0.30 |
| 305 | 50 | 0.06 |
| 310 | 200 | 0.015 |
| 315 | 1000 | 0.003 |
2. Permitted tolerant UV exposure
Table-1 shows a permitted tolerant value of UV exposure for each wavelength, which we call TLV (Threshold Limit Value) in accordance with the recommendation given by the ACGIH (the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists).
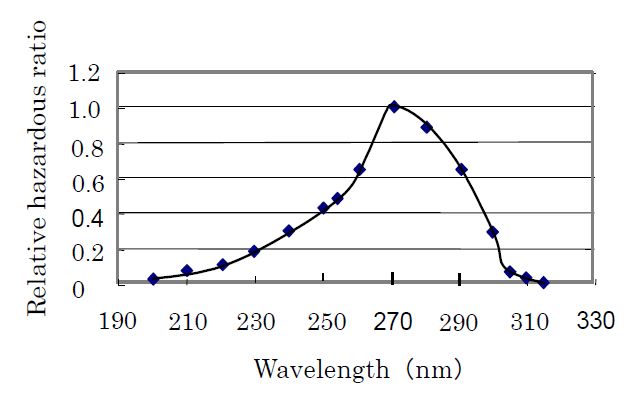
The most harmful wavelength is 270nm and its value of TLV is the lowest 3mJ/cm2. The figure 1 shows harmful ratio having relevance to the spectrum.
Fig 1. Relative hazardous ratio to the eye
3. Low Pressure Mercury Lamp
The main wavelengths of LP Hg lamp are 254nm and 185nm. The summed energy of both UV ray occupies 90% of the total radiation. The single 254nm radiation occupies 80% of the total energy. The wavelength of 254nm is so hazardous as well as a high energy ratio, you have to concentrate your protection measures only on the 254nm when you handle a low-pressure mercury lamp.
4. High Pressure Mercury Lamps
High pressure mercury lamps irradiate wider range of line spectrum and continuous wavelength, from UV to infrared. The main wavelength is 365nm. Unlike low pressure mercury lamps the high pressure mercury lamps have a lower 254nm ratio. In case of SEN Lights HL-100 lamp, only 8% of whole emission energy is from 253.7 to 276nm ray, but the danger is about 170 times of 315nm, for safety measures, it is rational to use 254nm as the standard rather than 365nm. High pressure mercury lamp irradiate many wavelength, hence to calculate the tolerated value, exposure value of each wavelength must be integrated. Practically, from dangerous point of view, overall exposure is about twice as that of 254nm, therefore half of tolerated value makes thing safety.
5. Calculation of intensity and exposure
The quantity of irradiated UV energy claims to be UV exposure and is measured in J/m2, but normally is shown in mJ/cm2. Practically, the strength of the UV ray is measured by its intensity.
UV power meter for 172nm, 185nm, 254nm and 365nm are sold on the market. The relation between exposure and intensity is shown in formula below.
UV exposure (mJ/cm2)=UV intensity (mW/ cm2) × Exposure time (sec)————————-①
By using this formula, in relation to working time, a safe intensity can easily be calculated. For example, for 254nm ray, tolerated TLV is 6mJ/cm2, 8 hours work TLV can be converted to, 6÷(8×60×60)≒0.000208, about 0.2μW/ cm2, which is the tolerated value of low pressure mercury lamp, half of this value, 0.1μW/ cm2 would be the tolerated value for high pressure mercury lamp.
6. Shield material and UV radiation permeability
UV radiation from 400nm to near 300nm permeates ordinary glass, but the 254nm UV ray doesn’t permeate the glass even 100% on the other hand, Synthetic quartz glass is the best permeable material. The permeability of 254nm wavelength differs drastically according to the material. Table 2 shows the permeability for several plastic material.
Table 2: Chart for 254nm permeability of different plastic & glasses
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Permeability (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
High Pressure Polyethylene Medium Pressure Polyethylene Low Pressure Polyethylene |
0.080 |
61.0 13.2 21.0 |
|
Polypropylene (Opaque) Polypropylene(Transparent) |
0.035 0.055 |
43.5 71.5 |
| Chloride Vinyl 【Flexible PVC】 Chloride Vinyl 【Rigid PVC】 Chloride Vinyl |
0.040 0.025 0.040 |
0.9 4.0 0.5 |
| Polyester Polycarbonate Polyamide Polystyrene |
0.050 0.030 0.035 0.050 |
0.5 5.5 28.0 0.5 |
| Vinegar Acid Scleroses Hydrochloric Acid Gum |
0.040 0.030 |
37.2 1.2 |
| Plain Cellophane Damp proof Cellophane (Chloride Vinyl) Damp proof Cellophane (Nitrocellulose) Damp proof Cellophane (Vinylidene) Polycellophane |
0.020 0.025 0.025 0.025 0.065 |
68.2 73.2 17.3 13.0 33.0 |
| Metaacrylic resin | 1.0 | 0 |
| Fused quartz glass Window glass |
2.5 1.0 |
90 0 |
